Key Points:
- Children with autism often struggle with social cues, conversations, and relationships, making social interactions challenging.
- Targeted strategies, such as visual supports, structured play, and social stories, can improve communication and engagement.
- ABA therapy provides structured interventions to help children develop and strengthen social skills over time.
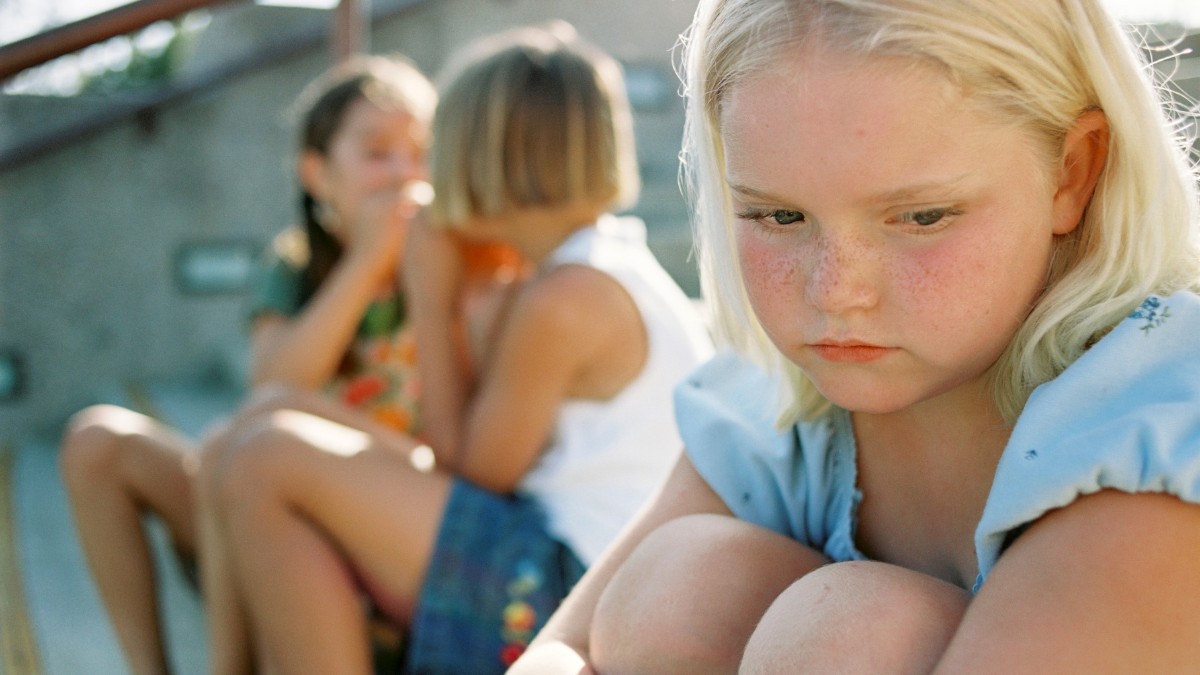
Making friends and socializing don’t come naturally to everyone. For children with autism, understanding social rules and cues can be challenging. However, with the right guidance—through structured play, social stories, and therapy—they can develop these skills and form meaningful connections in their own unique way.
What Are Social Interaction Difficulties in Autism?
Social interaction difficulties in autism refer to challenges in understanding, responding to, and engaging in social communication. Individuals with autism often struggle with nonverbal cues, turn-taking in conversations, and maintaining relationships.
Common difficulties include:
- Limited eye contact or facial expressions.
- Difficulty understanding emotions in others.
- Trouble engaging in back-and-forth conversation.
- Preference for solitary activities over social play.
- Literal interpretation of language, missing sarcasm or jokes.
These challenges vary by individual, with some children experiencing mild difficulties and others facing significant social barriers. Understanding these struggles is the first step in providing effective support.
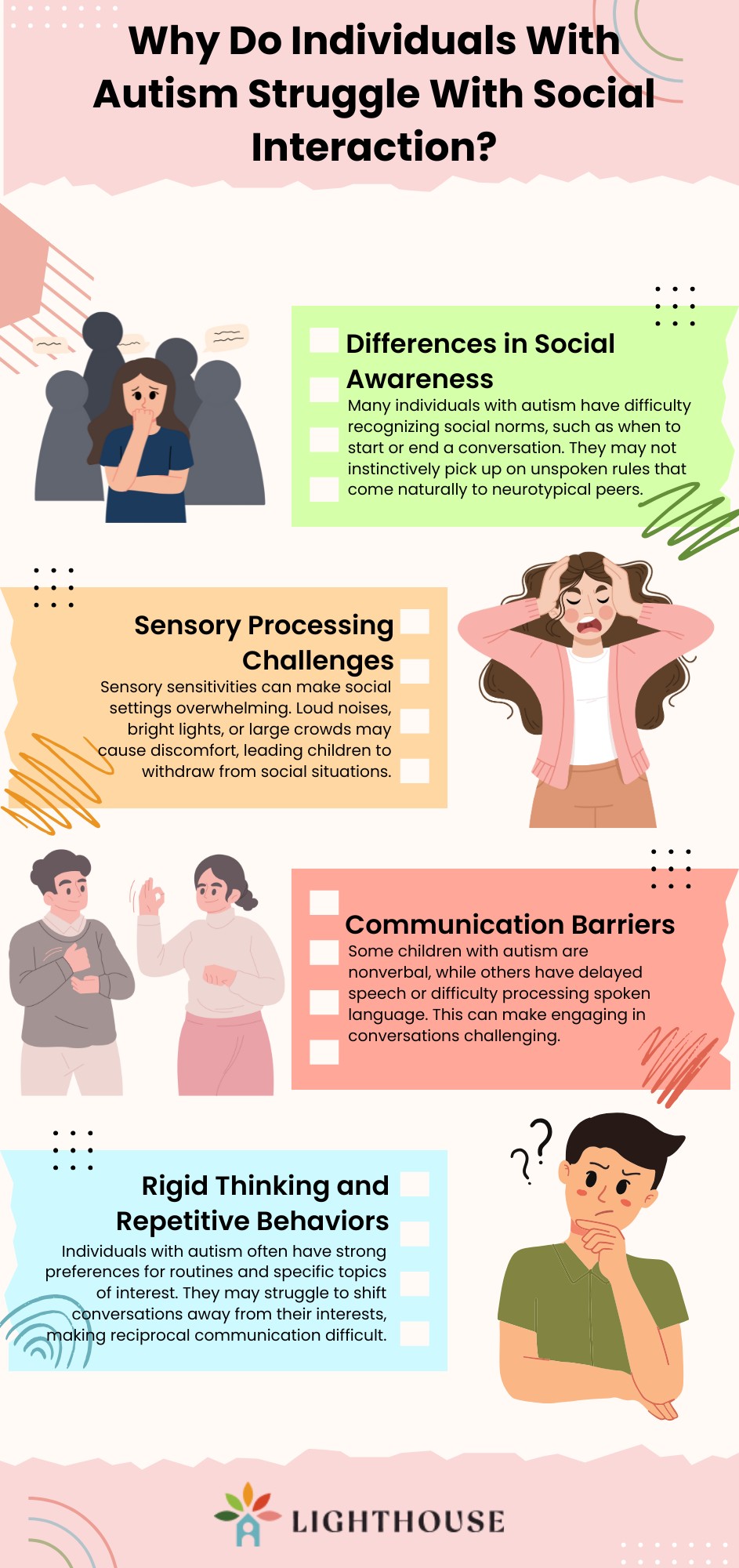
Why Do Individuals With Autism Struggle With Social Interaction?
Social interaction involves complex skills like reading body language, understanding tone, and responding appropriately in conversations. Children with autism may struggle in these areas due to:
Strategies to Improve Social Skills in Children With Autism
Improving social skills takes time, practice, and structured support. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Use Visual Supports
Many children with autism process information better visually than verbally. Tools such as:
- Social scripts (step-by-step guides for conversations).
- Picture exchange communication systems (PECS) for nonverbal children.
- Visual schedules to prepare for social situations.
These can provide clear expectations and reduce anxiety about interactions.
2. Practice Structured Play and Role-Playing
Social skills improve through repeated practice. Parents and therapists can:
- Guide children through structured play with peers.
- Use role-playing to model greetings, turn-taking, and asking questions.
- Encourage participation in group activities like board games or cooperative tasks.
This helps children gain confidence in social settings.
3. Introduce Social Stories
Social stories are short, personalized narratives that teach expected behaviors in various situations. These can:
- Explain how to handle common social scenarios (e.g., introducing yourself, making friends).
- Reduce anxiety by preparing children for new experiences.
- Reinforce appropriate emotional responses to different situations.
4. Encourage Peer Interaction in Small Steps
Jumping into large social groups can be overwhelming. Instead, start with:
- One-on-one playdates with structured activities.
- Small group settings with clear rules and guidance.
- Opportunities to interact with siblings or familiar adults first.
Gradually increasing social exposure helps build confidence.
5. Provide Positive Reinforcement
Acknowledging and rewarding social efforts helps children stay motivated. Use:
- Praise for attempting to engage in conversation.
- Reward charts for social goals, like making eye contact.
- Preferred activities as reinforcements for practicing new skills.
Reinforcement encourages continued social participation.
How Can ABA Therapy Help With Social Interaction Challenges?
ABA therapy is one of the most effective ways to help children with autism improve their social skills. It breaks social behaviors into small, teachable steps, making it easier for children to learn, practice, and apply these skills in everyday situations.
One of the main focuses of ABA therapy is teaching fundamental social skills, such as making eye contact, greeting others, and engaging in conversations. Therapists use structured methods, including modeling and role-playing, to help children understand and practice these essential interactions.
ABA also supports language and communication development, which is crucial for social interaction. Whether a child is verbal or nonverbal, ABA techniques like prompting, shaping, and reinforcement can help improve their ability to express needs, respond to questions, and engage with peers more effectively.
Another key aspect of ABA therapy is helping children navigate group settings. Many children with autism struggle with turn-taking, sharing, and teamwork. ABA sessions often include structured group activities where children can practice these skills in a controlled environment before applying them in school or play settings.
Finally, ABA focuses on real-life social situations by using natural environment training. This helps children apply their learned skills in everyday scenarios, such as ordering food, playing with friends, or joining conversations. Over time, these strategies help children build meaningful connections and interact more confidently.

Supporting Social Growth at Home and in the Community
Parents also play a critical role in helping their children develop social skills. In addition to professional therapy, here are ways families can encourage progress at home:
- Model appropriate social behaviors through daily interactions.
- Encourage participation in extracurricular activities like art, sports, or music groups.
- Expose children to diverse social settings gradually, ensuring comfort and readiness.
- Use everyday moments (e.g., grocery shopping, family meals) to practice greetings and small talk.
Community involvement also helps children generalize skills beyond the home. Libraries, autism-friendly events, and inclusive social groups can provide opportunities to practice social engagement in a supportive environment.
Partner with Lighthouse for Social Skills Development
Helping a child navigate social interaction difficulties in autism takes patience, strategy, and the right support system. With structured intervention, children can build the confidence and skills needed to connect with others.
At Lighthouse, we specialize in helping children with autism strengthen their social abilities through evidence-based ABA therapy. Our team works closely with families to create personalized treatment plans that foster meaningful social growth.
If you’re looking for professional ABA therapy services in New York City, we’re here to support your child’s journey toward better communication and social interaction. Contact us today to learn more!


